In the hustle and bustle of modern life, dishwashers have become indispensable appliances for many households. They save us time, conserve water, and make the daunting task of washing dishes effortlessly. While dishwashers are a common kitchen feature, not everyone understands how they work. Whether you’ve recently purchased your first dishwasher or are just curious about its mechanics, understanding the inner workings of a dishwasher can help you optimize its use, troubleshoot potential issues, and keep it functioning smoothly.
In this guide, we will walk you through the basic components, operational process, water usage, energy efficiency, and troubleshooting tips for dishwashers. We’ll also answer common questions like the best time to run a dishwasher, how energy-efficient dishwashers are, and much more.
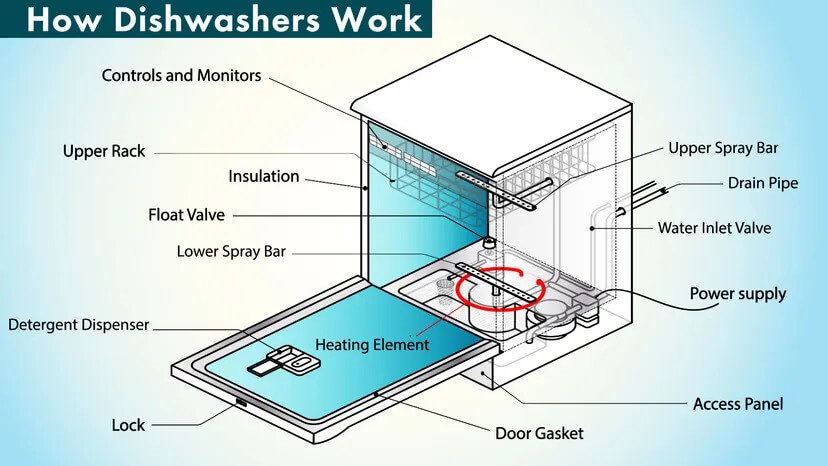
Basic Components of a Dishwasher
Understanding the basic components of a dishwasher is crucial for grasping how it functions. Each part has a specific role, contributing to the machine’s overall performance:
- Controls and Monitors: These are often located on the front or top panel of the dishwasher. They allow you to select different wash cycles, adjust the temperature, and monitor the cycle’s progress. Modern dishwashers often feature LED or digital displays, giving you more control over the wash.
- Upper and Lower Racks: The racks hold your dishes in place during the wash cycle. The upper rack is typically designed for smaller items such as glasses, cups, and smaller bowls, while the lower rack is used for larger items like dinner plates, pots, and pans. Some dishwashers come with adjustable racks, allowing for flexible loading configurations.
- Spray Arms: The spray arms rotate during the wash cycle, distributing hot water and detergent evenly across the dishes. Dishwashers commonly have two spray arms: one at the bottom and one underneath the upper rack. Some advanced models even have a third spray arm for more thorough cleaning.
- Detergent Dispenser: The detergent dispenser holds the detergent, whether it’s powder, liquid, or a pod. It is typically split into two compartments: one for detergent and one for rinse aid, which helps in drying dishes without water spots.
- Heating Element: Located at the bottom of the dishwasher, the heating element heats the water to the appropriate temperature for cleaning. It also helps in the drying phase by heating the air inside the machine.
- Float Valve: The float valve is a safety device that regulates water levels within the dishwasher, preventing overfilling. It works in tandem with the water inlet valve to ensure that just the right amount of water is used during each cycle.
- Drain Pipe: The drain pipe expels the dirty water from the dishwasher once the wash cycle is completed. It is connected to the plumbing system under your sink and carries away all food particles, detergent residue, and water.
- Water Inlet Valve: This valve allows water to flow into the dishwasher when needed. It opens and closes during the cycle, ensuring water is introduced at the correct stages for washing and rinsing.
- Door Gasket: This rubber seal around the door prevents water from leaking out during the wash cycle. If your dishwasher starts leaking, this is one of the first components to check for wear and tear.
- Power Supply: The power supply delivers electricity to the dishwasher’s control system, heating element, and motor, powering the entire cleaning process.
The Dishwasher Cycle: From Start to Finish
Dishwashers operate in a series of phases that work together to ensure your dishes come out spotless. Understanding these phases can help you better use your dishwasher, ensuring optimal cleaning results.
- Pre-Wash Phase: During the pre-wash phase, water enters the dishwasher and is sprayed onto the dishes to remove any loose food particles. This initial rinse helps prepare the dishes for the main wash by softening stuck-on food.
- Main Wash Phase: The detergent dispenser opens, releasing the detergent. Water is heated to a high temperature, usually between 120°F and 160°F (50°C to 70°C). The spray arms rotate, spraying hot, soapy water onto the dishes. The detergent breaks down grease and food particles, leaving the dishes clean.
- Rinse Phase: Once the main wash phase is complete, the dirty water is drained, and freshwater enters the dishwasher for rinsing. This rinse cycle may be repeated several times, ensuring all soap and residue are removed.
- Final Rinse with Rinse Aid: During the final rinse, some dishwashers introduce rinse aid into the water. Rinse aid reduces surface tension, preventing water droplets from forming on the dishes and promoting faster drying.
- Drying Phase: In the drying phase, the heating element warms the air inside the dishwasher, drying the dishes. Some dishwashers use a fan to circulate the hot air, while others rely on residual heat from the wash cycle. Models with energy-efficient settings may offer air-dry options, where no additional heat is used.

Water and Energy Efficiency: A Green Choice
Dishwashers are designed to use water and energy more efficiently than washing dishes by hand. Understanding their water and energy consumption can help you reduce your utility bills while making an environmentally friendly choice.
Dishwasher Water Temperature
The temperature of the water in a dishwasher is crucial for its performance. Most dishwashers heat water to a temperature of around 120°F to 160°F (50°C to 70°C). This higher temperature is more effective at breaking down grease and sanitizing dishes compared to handwashing, where water typically doesn’t exceed 100°F (37°C).
For optimal cleaning, ensure your dishwasher has a built-in heating element or a booster heater. This will ensure the water reaches the necessary temperature, even if your home’s water heater is set at a lower level.
How Much Water Does a Dishwasher Use?
Modern dishwashers are designed to be water-efficient, using as little as 3 to 5 gallons (11 to 19 liters) of water per load. Older models may use significantly more water, but even they are generally more efficient than handwashing, which can use up to 27 gallons (102 liters) for washing dishes manually.
By using less water, dishwashers help conserve this precious resource, making them an eco-friendly choice for your kitchen.
How Energy Efficient Is a Dishwasher?
Dishwashers are highly energy-efficient appliances, especially when compared to washing dishes by hand. A modern dishwasher with an Energy Star rating uses less than 1 kWh per load, whereas handwashing can use up to 2.5 kWh of energy when accounting for water heating. This energy saving makes dishwashers a better choice for both the environment and your electricity bill.
Energy-efficient dishwashers often have eco-friendly modes that use less water and energy for lightly soiled dishes. These modes can significantly reduce the cost of each load, making it cheaper to run the dishwasher than to handwash your dishes.
Dishwasher Cycles Explained
Dishwashers come equipped with various cycles to handle different types of loads and soil levels. Let’s dive deeper into the common cycles available in most modern dishwashers:
- Normal Cycle: The go-to cycle for everyday dishwashing. This cycle includes all phases: pre-wash, main wash, rinse, and dry. It is designed to clean moderately soiled dishes.
- Heavy Cycle: Ideal for heavily soiled pots, pans, and dishes with baked-on food. This cycle uses higher water temperatures and runs for a longer duration to ensure tough stains are removed.
- Quick Wash Cycle: This short cycle is perfect for lightly soiled dishes that don’t require a full-length wash. It typically skips the pre-wash and uses less water, making it faster and more energy-efficient.
- Eco-Cycle: Designed to save water and energy, the eco cycle operates at lower temperatures and uses less water, which extends the cleaning time slightly. This option is best for lightly soiled dishes.
- Rinse-Only Cycle: Some dishwashers come with a rinse-only cycle, which rinses the dishes without using detergent. This is useful when you want to rinse off food particles but aren’t ready to run a full cycle.
Dishwasher Tips: Improving Performance and Efficiency
Here are some key tips that can help you get the most out of your dishwasher:
- Pre-rinse sparingly: Many modern dishwashers come with sensors that adjust the cycle based on the dirt level of the dishes. Pre-rinsing can confuse these sensors, leading to less efficient cycles.
- Use the right detergent: Always opt for high-quality dishwasher detergent. Powders, liquids, and pods are formulated differently, so choose the one that works best with your machine.
- Load your dishwasher correctly: Ensure that your spray arms can move freely and that dishes are loaded in a way that allows water to reach all surfaces. Overloading or blocking the spray arms can reduce cleaning efficiency.
Best Time to Run a Dishwasher
When is the best time to run your dishwasher? Running your dishwasher during off-peak hours can save on electricity costs, as utility companies often charge less for energy during the late evening or night. Additionally, modern dishwashers come with a delay-start feature that lets you run the machine at a time that’s convenient for you or when energy costs are lower.
Can You Open Your Dishwasher Mid-Cycle?
Yes, it is possible to open the dishwasher mid-cycle, but caution should be exercised. When you open the door, the dishwasher will automatically pause, stopping the spray arms and other functions. Be aware that steam may escape when the door is opened, so take care to avoid burns. Once the door is closed, the dishwasher will resume the cycle from where it left off.
Common Dishwasher Problems and Troubleshooting Tips
Even with proper maintenance, dishwashers can encounter issues from time to time. Here’s a look at some common problems and troubleshooting tips:
- Dishes aren’t coming out clean: This is one of the most common complaints. Check for blocked spray arms, make sure the filter is clean, and ensure you’re using the right detergent. Overloading the dishwasher can also prevent proper cleaning.
- Dishwasher won’t drain: If water is pooling at the bottom of your dishwasher, check for blockages in the drainpipe or filter. The float valve could also be stuck, preventing the machine from draining properly.
- Dishwasher is making strange noises: Unusual sounds could indicate a loose spray arm, motor issues, or even utensils that have fallen out of the rack. Inspect the inside of the dishwasher for loose items.
- Leaking water: Leaks are often caused by a damaged door gasket or a faulty float valve. Inspect the door seal for wear and tear, and consider replacing it if necessary.
Advanced Features in Modern Dishwashers
Modern dishwashers come with a variety of advanced features aimed at improving their functionality and convenience. Some of these features include:
- Smart Technology: Many modern dishwashers come with Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing you to control and monitor the dishwasher via a smartphone app. This feature enables you to start a cycle remotely, receive notifications when a cycle is finished, and troubleshoot issues through the app.
- Sensor-Based Wash Cycles: Advanced dishwashers have sensors that detect the level of dirt on the dishes. The machine will adjust the cycle length, water temperature, and water usage based on how dirty the load is.
- Third Rack: Some dishwashers now feature a third rack at the top, designed specifically for utensils and smaller items. This not only increases your dishwasher’s capacity but also allows for better water flow, improving the cleanliness of your dishes.
- Sanitize Cycle: For families with infants or those who require a higher level of cleanliness, some dishwashers come with a sanitize option. This cycle heats the water to a very high temperature, killing bacteria and sanitizing your dishes.
Dishwasher Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your dishwasher and ensure it performs optimally. Here are some tips for maintaining your dishwasher:
- Clean the filters regularly: Dishwasher filters catch food particles and prevent them from being redeposited on your dishes. Regularly cleaning these filters can prevent clogs and improve water drainage.
- Run empty cycles with vinegar: Every few months, run a cycle with a cup of white vinegar. This helps remove any build-up of grease, food particles, or soap scum and keeps your dishwasher smelling fresh.
- Inspect spray arms: Check the spray arms for any food particles or debris that may be clogging the nozzles. You can remove and clean the spray arms to ensure they are rotating properly and providing adequate water pressure.
- Check the door gasket: The rubber gasket around the door should be checked regularly for signs of wear and tear. If you notice any cracks or damage, consider replacing the gasket to prevent leaks.
Conclusion: Why Dishwashers are a Must-Have in Modern Kitchens
Dishwashers are not only convenient appliances but also help conserve water, save time, and improve hygiene in your kitchen. By understanding how dishwashers work, you can take advantage of their full capabilities and ensure your dishes come out sparkling clean every time.
Whether you’re running a quick wash for lightly soiled dishes or tackling tough stains with a heavy cycle, knowing the ins and outs of your dishwasher will make your life easier. From optimizing loading techniques to troubleshooting common issues, this guide has covered everything you need to keep your dishwasher functioning at its best.
By following the tips and insights provided, you’ll be well-equipped to get the most out of your dishwasher while minimizing your environmental footprint. After all, dishwashers do more than just clean—they save time, conserve water, and make the kitchen a more pleasant place.




